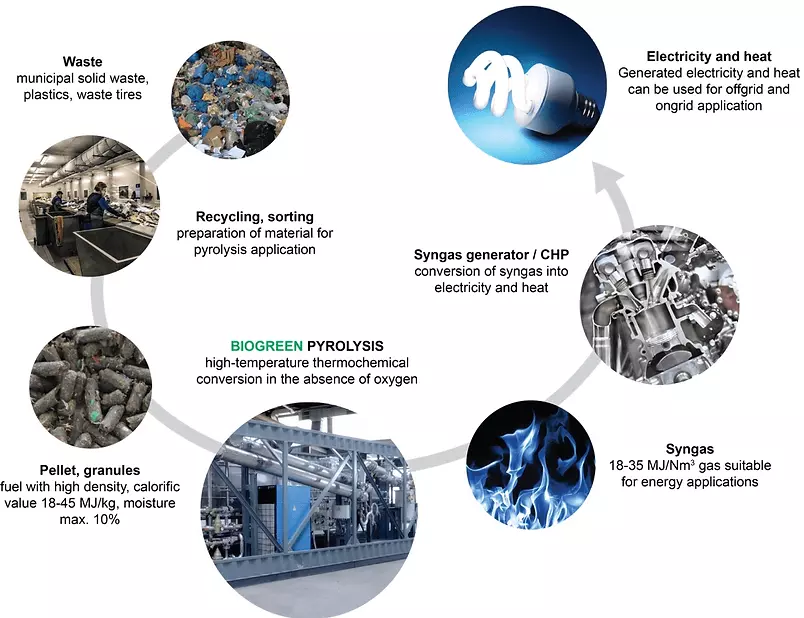
Waste Management System
B&F
Consulting is a leading global provider of environmental consultancy services with our Global Consulting Partners to the waste and recycling sector, providing advice to a range of clients including waste producers, the waste management industry, its regulators and investors.
The waste management philosophy developed by B&F Consulting follows an established waste hierarchy of waste prevention, minimization, reuse, recycling, energy recovery and final disposal.
The global B&F team has experience of providing practical advice on all waste types, including municipal, household, commercial, industrial, hazardous, agricultural, and, mining waste.
Air Solution
As consultants specializing in Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) projects, we propose a transformative initiative aimed at mitigating air pollution originating from mud brick factories in Bangladesh. Our strategy involves transitioning these polluting facilities into cement concrete brick factories, which do not rely on coal as a fuel source. This transition promises a substantial reduction in carbon dioxide emissions, aligning with the nation’s commitment to address climate change as outlined in its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
Our proposed approach entails a comprehensive process:
1. Assessment: Conduct a thorough evaluation to gauge the feasibility and potential impact of converting mud brick factories to cement concrete brick factories.
2. Technological Transition: Select and implement appropriate technologies and methodologies for the manufacturing processes of cement concrete bricks, emphasizing energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Secure the necessary permits and approvals from regulatory bodies to initiate and operate cement concrete brick factories, ensuring adherence to environmental standards and regulations.
4. Financial Support: Source funding through various channels, including grants, loans, or partnerships, to facilitate the conversion process and support sustainable operations.
5. Infrastructure Development: Develop or modify infrastructure to accommodate the requirements of cement concrete brick production, encompassing raw material storage, mixing, molding, curing, and transportation.
6. Capacity Building: Provide training and skill development programs to empower the workforce with the knowledge and capabilities essential for efficient and effective operation of cement concrete brick factories.
7. Environmental Impact Mitigation: Implement measures to mitigate any potential adverse environmental impacts associated with the transition, focusing on minimizing emissions, waste generation, and resource consumption.
8. CDM Application: Prepare and submit a comprehensive CDM project proposal to the Bangladesh Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) for endorsement, highlighting the emissions reduction potential and sustainable development benefits of the initiative.
9. Monitoring and Reporting: Establish robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms to track progress, evaluate performance, and ensure compliance with CDM requirements, providing regular updates to relevant stakeholders.
10. Stakeholder Engagement: Foster engagement and collaboration with stakeholders, including local communities, government agencies, and non-governmental organizations, to promote transparency, inclusivity, and shared ownership of the initiative’s objectives and outcomes.
Through strategic planning and concerted efforts, our proposed initiative aims to effect meaningful change by addressing air pollution, reducing carbon dioxide emissions, and advancing sustainable development in Bangladesh, thereby contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
Water Solution
- Coagulation and Flocculation:
are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water. The positive charge of these chemicals neutralizes the negative charge of dirt and other dissolved particles in the water. When this occurs, the particles bind with the chemicals and form larger particles, called floc. - Sedimentation:
During sedimentation, floc settles to the bottom of the water supply, due to its weight. This settling process is called sedimentation. - Filtration:
Once the floc has settled to the bottom of the water supply, the clear water on top will pass through filters of varying compositions (sand, gravel, and charcoal) and pore sizes, in order to remove dissolved particles, such as dust, parasites, bacteria, viruses, and chemicals. - Disinfection:
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.



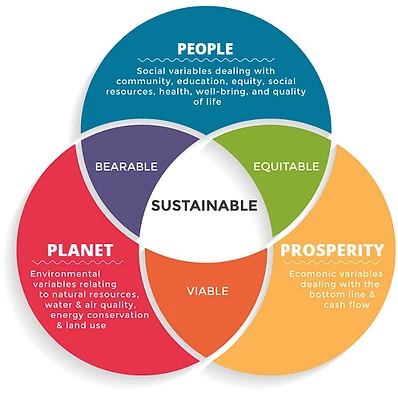
Sustainable Environment Projects
- Sustainability is only for energy and environmental solutions: Sustainability is a process for capturing all internal and external resources for optimization. Organizations can limit sustainability to energy, energy efficiency, environment, carbon capture, emissions but more so, sustainability distills down the simplest node of an organization for effectiveness.
- Sustainability is perceived as a big or large organizational construct: Sustainability can be used by a one man shop or a transnational corporation. The differences are represented by their ecosystem and supply chain. Sustainability identifies stakeholders, ecosystem and supply chains across platforms, systems and processes for a new lens to durability, longevity and profitability.
- Sustainability is for people who believe in green. Sustainability are for people who believe in considering tomorrow in their present operations. If you as a leader have an organization that you consider only today and tomorrow is not relevant then yes, sustainability is not for you. Sustainability is a working mechanism aggregating and defining elegant solutions.
- Sustainability is not used by technology companies. Technology companies are indeed driven by sustainability as the torrent of data, systems, energy and innovation push out and into these organizations. Consider, Google, Yahoo and more who have formed alliances to determine how to gain energy, solutions and requirements to service their systems for tomorrow. These companies are tooling to build smart grid solutions that indeed will aid other surrounding organizations producing sustainable solutions.
BnF projects on SEP
Conduct Feasibility study and preparation of Layout Plan
– Preliminary conceptual drawings for the proposed land use of Matuail Sanitary Landfill Area
– Create 3D Animation
Land use plan of existing Sanitary Landfill site and proposed
– considering all environmental issues and conditions specificto Bangladesh

